Present Time 3
Present Simple: Frequency adverbs
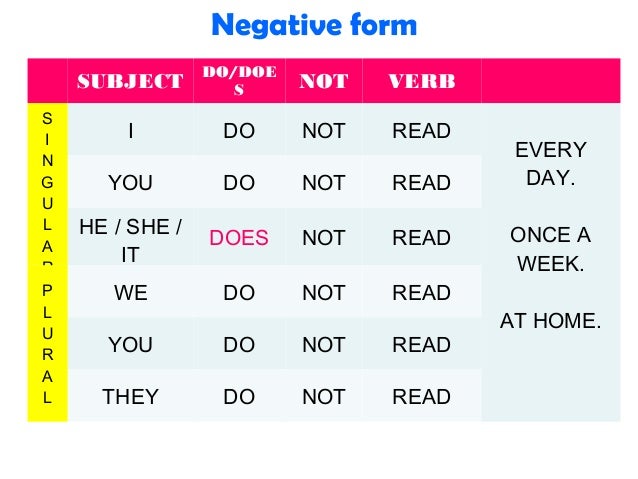
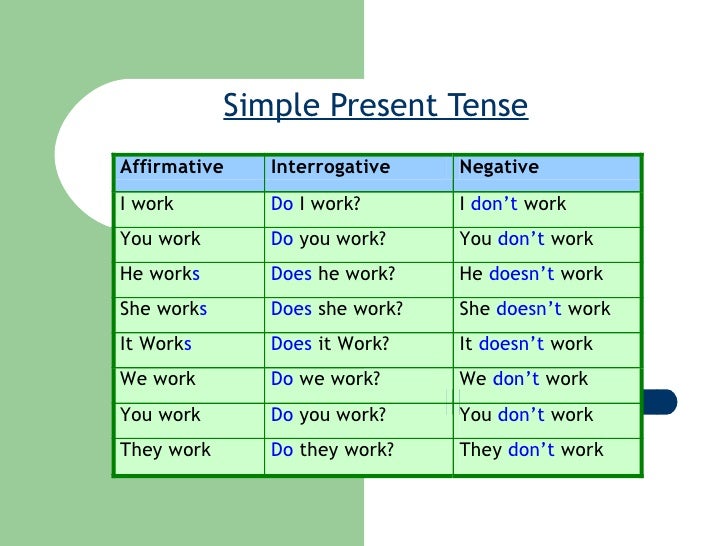
* Frequency adverbs are often used with the Present Simple. They explain how often someone does an action or something happens.
Examples:
* I always get up at 5:00 AM.
* Danny often goes to football games.
* It usually rains when I take a vacation!
* We sometimes eat pizza for lunch.
* John rarely listens to jazz.
* My friend never arrives on time.
- Note that the frequency adverb usually goes between the subject and the verb.
- Frequency adverbs used with the verb "be" come after the verb.
- Jim is usually late.
State and event verbs
- Some verbs are usually used in present simple and not in present continuous. These are sometimes called state verbs because they describe continuing states, not sudden action
- having and being: belong to contain, cost, depend on, have, own.
- Thinking and feeling: believe, forget, like, hate, know, prefer, understand.
- Some verbs are more common as state verbs in present simple, and change their meaning when they are used as event verbs in present continuous.
Event verbs describe actions.
I have two sisters. (permanent)
I´m having problems with this computer. (a temporary action)
Examples include Be, have, taste, think.
- Some state verbs can be used to describe temporary feelings.
How are you doing with your English conversation?
I am understanding more and more!